Deep Decarbonization: The Key to Sustainability
Arguably the most urgent challenge confronting humankind today is the issue of climate change.
The persistent utilization of fossil fuels throughout society, and the need for continued growth, has resulted in elevated global temperatures, severe weather occurrences, and numerous destructive effects on our planet.
To counter this alarming situation, deep decarbonization is needed.
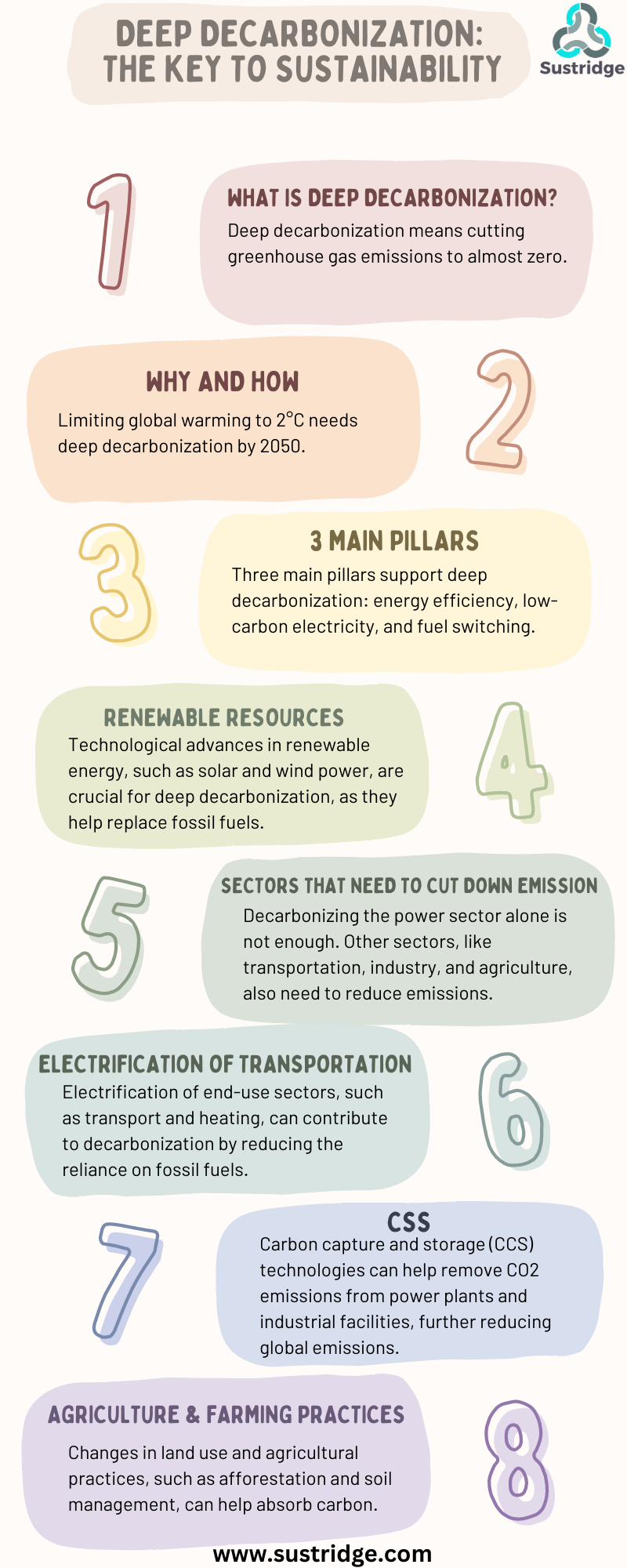
Infographic on the details of Deep Decarbonization
What is Deep Decarbonization?
Deep decarbonization is a crucial method for diminishing greenhouse gas emissions, reversing the destruction cycle, and for the overall sustainable development of earth.
Deep decarbonization is essential for realizing significant reductions in worldwide emissions, including indirect emissions, and safeguarding our planet’s long-term well-being. By overhauling our energy infrastructure and adopting sustainable alternatives across society, such as renewable energy and regenerative agriculture, we can address the escalating issues our planet is facing from problematic sectors such as the energy industry, industrial agriculture, and transportation.
In this blog, you will uncover the relevance of deep decarbonization, along with practical examples, and cutting-edge studies to help you make sustainable choices.
Whether you're an entrepreneur, consultant, or simply an individual passionate about tackling the climate emergency, hopefully, this blog will serve as an invaluable resource, enlightening you on pressing issues and offering insights into potential solutions.
A study by the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) highlights the importance of significantly decarbonizing our energy infrastructure in order to curb global warming and alleviate the catastrophic consequences of climate change (IPCC, 2018).
Join us on this journey to examine the potential and challenges of deep decarbonization, and find out how you can participate in building a sustainable future for everyone.
Understanding Deep Decarbonization
Path to Decarbonization is the pathway to a sustainable future
Deep decarbonization refers to the process of achieving near-zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from all economic sectors, including energy production, transportation, agriculture, and industry. This is a crucial step in addressing climate change, as it would substantially reduce atmospheric carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases.
The devastating effects of climate change are one of the primary reasons why thorough decarbonization is absolutely essential.
Rising temperatures, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events are just a few of the consequences of global warming that we are already experiencing. But all hope is not lost. Experts say we can still defend the planet for future generations by reducing our GHG emissions.
The Role of Deep Decarbonization in Climate Change Mitigation
It is simple actually. To tackle climate change, all we have to do is to focus on cutting down carbon emissions big time. It's a key part of the solution!
Improving Energy Efficiency
It involves transitioning away from fossil fuels and replacing them with cleaner, more sustainable sources of energy. By doing so, we can significantly reduce our carbon footprint and limit the amount of greenhouse gasses we emit into the atmosphere.
One of the ways in which we can achieve deep decarbonization is by investing in renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower. These sources of energy are not only cleaner than fossil fuels, but they are also becoming increasingly affordable and accessible. In fact, in many parts of the world, they are already cheaper than traditional energy sources.
Deep decarbonization also emphasizes making changes to the way we consume and use energy. This includes improving energy efficiency in buildings and transportation, reducing waste, and promoting sustainable agriculture and forestry practices.
Another important aspect of deep decarbonization is the need for international cooperation and collaboration. Climate change isn't a local problem, but a global one, and thus it requires a global solution to defeat it. This means that countries must work together to develop and implement effective deep decarbonization strategies that can reduce greenhouse gas emissions on a global scale.
Pathways to Deep Decarbonization
As the world continues to grapple with the impact of climate change, it is becoming clearer that deep decarbonization is necessary to mitigate its effects.
For business owners, sustainability consultants, and the general public, deep decarbonization pathways offer unique ways to reduce emissions in different sectors. For instance, the power sector can benefit from solar and wind energy, while the transportation sector can shift to electric vehicles. By focusing on energy efficiency, low-carbon electricity, and fuel switching, we create a framework for decarbonization across industries.
A. Energy Efficiency and Conservation
A powerful method to reach deep decarbonization is by boosting energy efficiency and drastically reducing our energy needs, as well as embracing cleaner energy sources like wind and solar power.
Deep decarbonization is possible by improving energy efficiency
This means using energy wisely in our homes, workplaces, and transport systems, while cutting energy waste by enhancing building standards and refining industrial processes.
For instance, choosing LED light bulbs, employing smart thermostats, and insulating buildings can greatly cut energy use, which in turn lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
Shifting from fossil fuels to natural gas can also contribute to a slight reduction in emissions, as natural gas is a cleaner alternative with lower carbon content. However, there are still emissions associated with natural gas so it should be thought of as a transition fuel, until society can operate on 100% clean and renewable energy.
Additionally, energy efficiency and reduced energy demand come with financial perks. By consuming less energy and investing in solar power, people and businesses save money on their bills, which can then be spent in other parts of the economy. Together, these efforts bring us closer to a zero-emissions future.
B. Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable Energy Sources
A vital step towards deep decarbonization is using renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy. These clean, sustainable options emit little to no greenhouse gasses.
Transforming energy systems to incorporate renewable power plays a significant part in combating climate change. By replacing fossil fuels with clean sources like solar and wind, we can reduce warming gasses released into the atmosphere.
Solar power has become an increasingly popular choice for homes and businesses to reduce carbon emissions. By installing solar panels, individuals and organizations can generate their own clean, zero-emissions electricity.
Renewable energy use is quickly expanding worldwide, with many countries setting bold goals to boost their renewable energy share.
For instance, Germany leads the way in transitioning to renewables, targeting at least an 80% share by 2050 with their "Energiewende" policy.
Similarly, Denmark has committed to a 100% renewable energy supply by 2050, with wind energy playing a significant role.
Scotland successfully generated 97.4% of its electricity demand from renewables in 2020, mainly due to its vast wind and hydro resources.
As more countries embrace renewable power, we move closer to a future with lower warming gasses and a cleaner, greener planet.
Besides cutting greenhouse gas emissions, renewables offer many benefits. They generate new jobs, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and enhance energy security by diversifying sources.
C. Carbon Capture and Storage Technologies
Process of Carbon Capture and Storage
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) methods catch carbon dioxide emissions and store them underground or in other lasting facilities. These techniques lessen greenhouse gas emissions' effects and play a vital role in deep decarbonization. CCS is especially crucial for hard-to-decarbonize industries like cement, steel, and chemicals.
The Sleipner project in Norway has successfully stored over 20 million tons of CO2 in an offshore saline aquifer since 1996, demonstrating the potential of CCS. These initiatives, combined with renewable power, pave the way for zero carbon electricity.
The Boundary Dam project in Canada, which captures CO2 from a coal-fired power plant and stores it in nearby oil fields is another successful implementation of CCS.
CCS technologies are still developing, currently facing considerable technical and economic hurdles and there are worries about the safety and lasting reliability of underground storage sites.
D. Electrification and Decarbonization of Transportation
Electric cars help lower emissions, reduce air and noise pollution in cities.
Transportation is a major source of global greenhouse gas emissions.
Making our transport systems greener by using electric vehicles or eco-friendly public transport, is crucial for cutting emissions and reaching deep decarbonization.
Electric vehicles are gaining popularity, and many countries are providing incentives for buying them and building charging stations. Besides lowering emissions, electric vehicles help reduce air and noise pollution in cities.
Eco-friendly public transport, such as buses and trains powered by renewables, also helps decarbonize transport. Active options like walking and cycling decrease car use and encourage healthier living.
For example, Norway has become a leader in electric vehicle adoption, with more than 65% of new cars sold in 2021 being electric.
In the United States, California's high-speed rail project aims to provide a sustainable, electric-powered alternative to air and car travel between major cities.
E. Revolutionizing Agriculture: Carbon Capture and the Energy Transition
The energy transition has brought about remarkable new technologies that help combat climate change and lower emissions back to pre-industrial levels. One such approach is altering land use and farming practices to better absorb carbon, which not only benefits our environment but also protects our well-being.
For instance, afforestation—planting trees on previously non-forested land—has proven to be an effective way to capture carbon while offering added perks like habitat creation and erosion control. Similarly, smart soil management techniques, such as no-till farming and cover cropping, can increase carbon sequestration and improve overall soil health.
Take the case of Costa Rica, which has made significant strides in reforestation and sustainable land management. Over the past few decades, the country has reversed deforestation rates and now boasts more than 50% of its land area covered by forests. These efforts not only help reduce carbon in the atmosphere but also support local economies, human health and biodiversity conservation.
What is Sustainability Revolution?
We live in an era in which businesses not only maximize profits, but also take extraordinary measures to defend the environment. The sustainability revolution has arrived and is transforming the way we conduct business and live our lives.
The sustainability revolution is a global movement toward ESG principles in which businesses and individuals place greater emphasis on sustainable practices. Companies such as Patagonia, with its "Repair, Reuse, Recycle" policy, and Unilever, with its pledge to halve its use of virgin plastic by 2025, are at the forefront of the movement. The revolution is about more than just "going green"; it's about establishing a future in which economic development and environmental protection coexist.
Consider, as a business owner or consultant, how adopting sustainable practices could enhance your brand's image, attract environmentally conscious consumers, and bolster your bottom line. According to the 2020 Cone/Porter Novelli Purpose Study, 66% of consumers would transition from a typical product to a new product from a purpose-driven company. This is definitely food for contemplation!
For the broader public, the sustainability revolution translates to more options and authority. You can now choose to support companies that share your values, thereby contributing to a healthier planet for future generations.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Policies and regulations are essential in driving deep decarbonization
Policies and regulations play a pivotal role in driving deep decarbonization.
By designing and implementing effective policies, governments can motivate businesses and individuals to lower their greenhouse gas emissions, accelerating the transition to a low-carbon economy.
In the United States, the Production Tax Credit (PTC) has spurred the growth of wind and solar power by making renewable energy more cost-competitive.
Three pillars are quintessential for a successful decarbonization strategy:
Engineering
Research Teams
Climate Policy
Quick fixes might offer some benefits, but to make a real difference, we need a consistent and all-encompassing plan. Take renewable energy, like wind and solar power, for example. We can only make these resources more effective and affordable by having dedicated researchers come up with creative solutions that combat climate change. It's crucial to have strong climate policies in place to encourage these changes across different industries.
For instance, governments can pour money into research to make green technologies cheaper and more available to everyone. By getting different groups—like businesses, schools, and lawmakers—to work together, we can come up with new ideas faster.
Governments can also set a good example by using renewable energy and energy-saving tech in public spaces, which might inspire companies to do the same.
Some really good examples of Government taking initiatives are:-
South Australia has embraced renewable energy and aims to reach 100% renewable electricity by 2030. The state has been investing in solar, wind, and battery storage technologies, with over 60% of its electricity generation coming from renewable sources in 2020.
Costa Rica aims to become carbon neutral by 2050, thanks to its focus on renewable energy and sustainable development. With over 98% of its electricity generated from renewable sources like hydropower, geothermal, wind, and solar, the country serves as an example of a successful transition.
So, to really tackle climate change, we need a combo of good engineering, dedicated research teams, and solid climate policies. This kind of environment will lead to better innovation and ultimately, a greener future.
Carbon Pricing and Emissions Trading
Carbon pricing and emissions trading are two effective ways to incentivize the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
Carbon pricing puts a price on carbon emissions through a carbon tax or a cap-and-trade system.
The European Union's Emissions Trading System (ETS), which puts a price on carbon, prompting businesses to adopt cleaner technologies and practices.It covers more than 11,000 power stations and manufacturing plants in 31 countries and has helped to reduce emissions in the EU by over 20% since its introduction in 2005.
Emissions trading allows companies to trade emissions credits, which can be bought and sold on a market.
Both policies create a financial incentive for companies to reduce their emissions, as those that emit less can sell their unused credits to those that emit more. This encourages companies to invest in low-carbon technologies and practices, and can help drive deep decarbonization.
Renewable Portfolio Standards
Renewable portfolio standards (RPS) are another policy tool that can help drive deep decarbonization.
RPS requires energy providers to generate a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources, such as wind, solar, and hydro power. These policies stimulate investment in renewable energy and drive innovation in the sector, helping to accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy.
For example, in the United States, 29 states and the District of Columbia have implemented RPS policies. As a result, renewable energy sources now account for over 10% of electricity generation in the country.
Energy Efficiency Standards and Incentives
Energy Efficiency Standards and Incentives
Energy-saving rules and rewards for eco-friendly gadgets, buildings, and transport can really help us cut down on carbon emissions and achieve our sustainability goals. By promoting and supporting energy-efficient tech, we can use less power and protect the planet at the same time.
Take the Energy Star program in the US, for example. It's managed by the Environmental Protection Agency and gives people incentives to buy green appliances and electronics. Since it started in 1992, this program has helped us avoid more than 2 billion metric tons of greenhouse gas emissions. That's a pretty big deal!
Japan's Top Runner Program sets energy efficiency standards for various products, like appliances, vehicles, and industrial equipment. These standards are based on the best-performing products in the market, so manufacturers are encouraged to keep innovating and improving energy performance. Since its launch in 1999, the Top Runner Programme has been estimated to have reduced energy consumption by 5% in road transport and by 8% in the residential sector.
These examples portray how different countries and regions are implementing policies and programs to encourage energy efficiency, ultimately contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.
Research and Development Support
Putting money into research and development is super important if we want to find new ways to cut down on carbon emissions. Both public and private funding can help us discover innovative solutions and get them out into the world faster.
Take a look at the US Department of Energy's ARPA-E, for instance. They fund bold research projects that could really change the game when it comes to energy. Since they started in 2009, they've poured over $2.5 billion into over 800 projects, and many of them could make a huge difference in reducing carbon emissions.
Challenges and Barriers to Deep Decarbonization
Tech Limitations
One of the biggest challenges to deep decarbonization is technological limitations. Although many renewable energy sources and carbon capture technologies are available, there are still significant gaps in our understanding and ability to implement them at scale.
Economic and Financial Constraints
Another significant barrier to deep decarbonization is the economic and financial constraints involved in transitioning away from fossil fuels. In many cases, renewable energy sources and other low-carbon technologies are more expensive than traditional fossil fuels, which can make their adoption challenging.
Social and Political Resistance
Social and political resistance are other significant barriers to deep decarbonization. Some people and organizations may resist the transition away from fossil fuels, either due to concerns over job losses or ideological opposition to certain policies and technologies.
Conclusion
Despite these challenges, deep decarbonization is absolutely essential for tackling climate change and creating a greener future. By demystifying our carbon emissions through meticulous carbon footprint analysis, we are navigating towards deep decarbonization, the keystone of our sustainable future.
Progress in technology, encouraging policies, and worldwide cooperation can help us conquer these obstacles and move towards a low-carbon economy. This is where sustainability firms like Sustridge come in.
Sustridge can play a significant role in helping companies reach deep decarbonization through their carbon accounting and management services and decarbonization consulting, roadmaps. By assisting businesses in measuring, tracking, reporting, and reducing their greenhouse gas emissions, our climate consultants can help create tailored sustainability strategies that lead to meaningful carbon reductions. We can also provide guidance on setting Science-Based Targets that align companies' decarbonization goals with global climate efforts, ensuring that their contributions are in sync with the larger mission of combating climate change and limiting global temperature increases.
By working with sustainability firms like Sustridge, businesses can effectively measure and reduce their carbon footprint, contributing to a more sustainable and low-carbon world.